Product of the Month
Featured Equipment, Products & Services
SEW-EURODRIVE’s X.e Series: Robust, High-Torque Drive Solutions for the Mining and Aggregate Industries
Bucket elevator and conveyor operation times in the mining and aggregate industries differ considerably concerning operating hours: some conveying systems only operate sporadically, while...
Nobel Fire Dyno Nobel’s Digital Platform
Who It’s For:
Nobel Fire is Dyno Nobel’s digital platform that seamlessly integrates with large operators’ complex digital ecosystems while simultaneously providing a holistic solution...
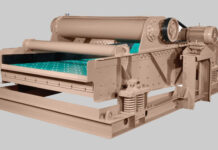
Deister Offers Super-Duty Dewatering Solution
Deister dewatering screens offer a super-duty dewatering solution that delivers cost-efficient processing with deeper beds of material, and at higher tonnages, versus that of...
Unlocking Maximum Crushing Efficiency: Value-Added Solutions for Success from ME Elecmetal
We design solutions to help our customers achieve their goals by combining wear parts with technology tools, advice, training, and monitoring — all of...
Dings Stationary Electromagnets
If Tramp Metal is Rare in Your Process but Must be Removed then… Sometimes Simpler is Better.
Dings Stationary Electromagnet Installed
Dings Overhead Stationary Electromagnet’s deep...
Advanced Detection Systems’ SurroundScan Protector Series: Metal Detection Engineered for Aggregates and Mining
Advanced Detection Systems’ Protector Metal Detectors are designed to detect ferrous, non-ferrous and stainless-steel metal in bulk material ensuring product purity and protecting processing...
Schurco Slurry V Series Cantilever Pump
Schurco Slurry’s V-Series cantilever slurry pump offers several advantages over vertical turbine and submersible pumps when handling abrasive slurries. There are no submerged bearings,...
Magnetic Drum Separators from Industrial Magnetics
IMI's Magnetic Drum Separators provide ferrous metal removal from dry, bulk products in free-flowing processing systems.
IMI's Magnetic Drum Separator
Magnetic drum separators are continuously...
Crisp Industries Specializes in Design and Construction of New Aggregate Material Systems
Crisp Industries specializes in design and construction of new aggregate material systems, as well as custom fitting major additions to customers’ existing operations. Our...
Richwood’s Complete Transfer Chute Design, A Practical Approach
Complete Transfer Chute Design, A Practical Approach
Persistent challenges in traditional chute design have been a long-standing concern—material blockages, improper loading on conveyors, excessive chute...
Stedman’s Mega-Slam™ Primary Horizontal Shaft Impactors (HSI)
Stedman Machine Company is a U.S.-based manufacturer of industry-leading, premium-impact-style crushers for the aggregate industry. We listen to our customers and develop custom solutions...